The Opioid Safety Program's mission is to reduce opioid misuse and abuse in Calaveras County.
The objectives of the program:
- Coordinate and develop a local opioid safety educational campaign.
- Educate community members on opioid safety.
- Educate first responders, emergency medical services, fire authorities, law enforcement, courts, and criminal justice partners, veteran organizations, homeless programs, schools and universities, libraries, religious entities, community organizations, substance use disorder recovery facilities, and hospital emergency departments on preventing opioid overdose.
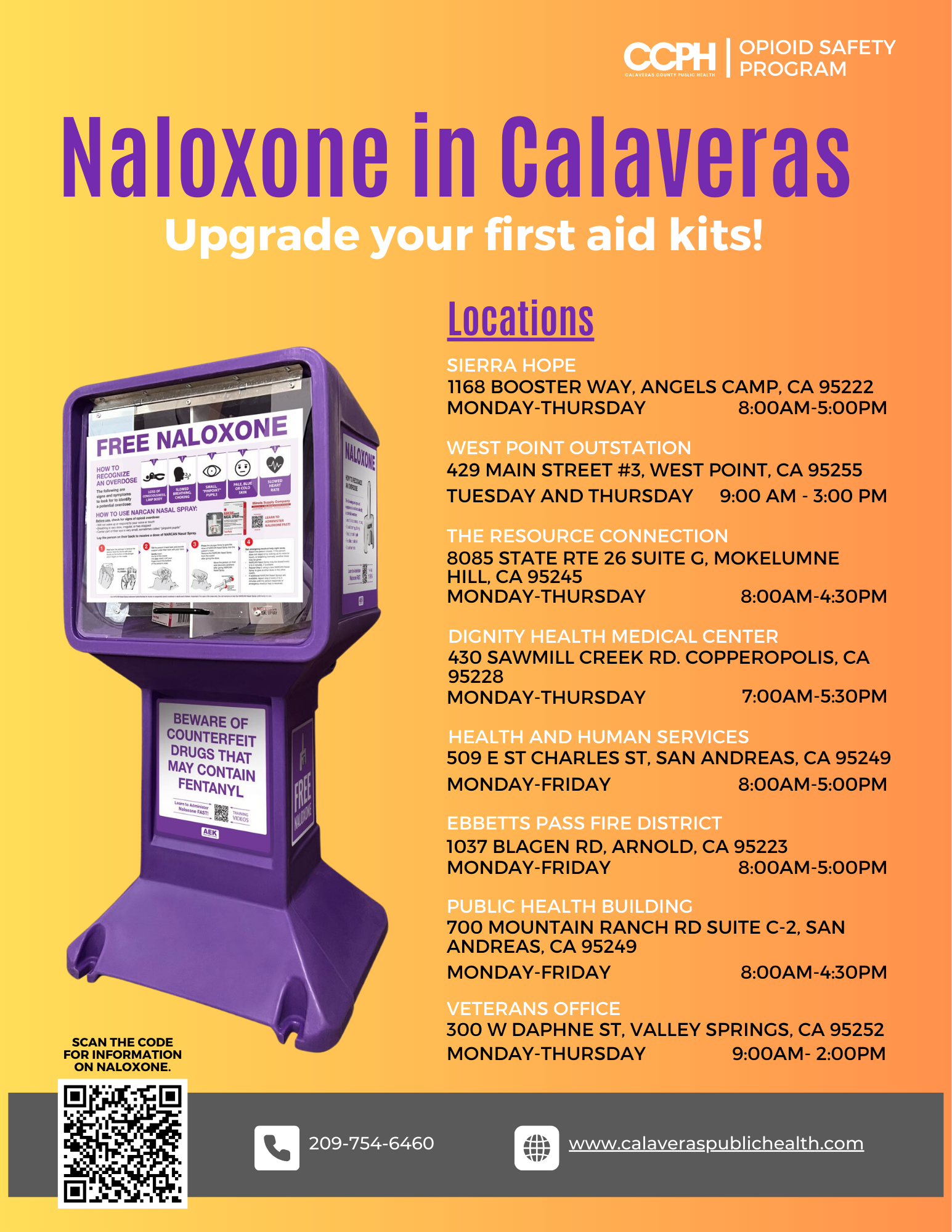
No-cost naloxone can be found in various locations throughout the county. Visit the Naloxone Kiosk Map to find a location near you.